These amounts are likely different from the amounts reported on the Travel Agency Accounting company’s income tax return. The dividends declared by a company’s board of directors that have yet to be paid out to shareholders get recorded as current liabilities. The current portion of long-term debt due within the next year is also listed as a current liability. Also, if cash is expected to be tight within the next year, the company might miss its dividend payment—or at least not increase its dividend.
- Taxes Payable refers to the taxes owed by a company to various tax authorities, such as federal, state, and local governments.
- The balance sheet (also known as the statement of financial position) reports a corporation’s assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity as of the final moment of an accounting period.
- Liabilities play a crucial role in evaluating a company’s financial health.
- Pension obligations are crucial to understanding a company’s commitment to its employees and the potential strain on future resources.
- A company’s assets are also grouped according to their life span and liquidity – the speed at which they can be converted into cash.
For Managing Cash Flow

A manufacturer must disclose in its financial statements the amount of finished goods, work-in-process, and raw materials. That part of a manufacturer’s inventory that is in the production process but not yet completed. This account contains the cost of the direct https://sadiqpaper.com/bookkeeping-for-interior-designers-what-a-top/ material, direct labor, and factory overhead in the products so far.

Types of Liabilities
Entities often use an amortization schedule, which breaks down each loan payment into its principal and interest components, to identify the principal portion due in the upcoming year. Conversely, companies might use accounts payable as a way to boost their cash. Companies might try to lengthen the terms or the time required to pay off the payables to their suppliers as a way to boost their cash flow in the short term.

How to do Account Payables balance sheet entries in the right way?
- They’re all about performance—revealing whether your business is rolling in dough or barely scraping by.
- In accounting, liabilities and expenses represent two distinct financial concepts.
- Debit the corresponding sub-asset account when you add money to it.
- For example, a manufacturing entity would be required to pay rent to the owner of its factory building and wages to its workers so as to carry on its production activities.
- Current liabilities are typically listed first, followed by non-current liabilities.
This article are expense accounts liabilities clarifies these accounting elements, explaining their individual characteristics and how they interact within a company’s financial records. Liabilities are carried at cost, not market value, like most assets. They can be listed in order of preference under generally accepted accounting principle (GAAP) rules as long as they’re categorized. The AT&T example has a relatively high debt level under current liabilities. Other line items like accounts payable (AP) and various future liabilities like payroll taxes will be higher current debt obligations for smaller companies. When presenting liabilities on the balance sheet, they must be classified as either current liabilities or long-term liabilities.
In accounting terms, leases can be classified as either operating leases or finance leases. An operating lease is recorded as a rental expense, while a finance lease is treated as a long-term liability and an asset on the balance sheet. They’re recorded in the short-term liabilities section of the balance sheet. Liabilities can also be classified as either interest-bearing or non-interest-bearing. Interest-bearing liabilities, such as loans or bonds, require the payment of interest over the term of the liability. Non-interest-bearing liabilities, on the other hand, do not involve an explicit interest component, such as accounts payable or accrued expenses.
- In short, a company needs to generate enough revenue and cash in the short term to cover its current liabilities.
- Expenses are recognized when they are incurred, regardless of when cash is actually paid, following the accrual basis of accounting.
- From the table above it can be seen that assets, expenses, and dividends normally have a debit balance, whereas liabilities, capital, and revenue normally have a credit balance.
- AT&T clearly defines its bank debt that’s maturing in less than one year under current liabilities.
- In addition to our balance sheet templates, our business forms also offer templates for the income statement, statement of cash flows, and more.
- The placement of expenses and liabilities on financial statements reinforces their distinct nature.
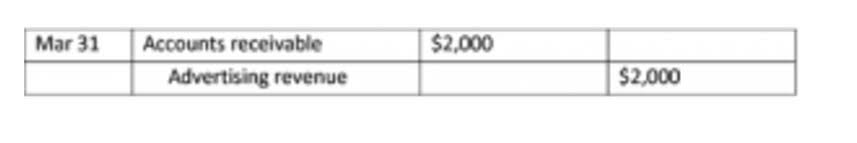
For accrued liabilities—those expenses you’ve incurred but haven’t paid yet—Ramp’s real-time visibility changes the game. The platform tracks all corporate card transactions and pending reimbursements in one place, giving you a complete picture of your outstanding obligations at any moment. You can see exactly what’s been spent but not yet paid, making month-end accruals straightforward instead of an exercise in detective work. Ramp even integrates with your accounting software to ensure these accruals flow seamlessly into your general ledger with the proper liability coding.
Most companies don’t pay for goods and services as they’re acquired, AP is equivalent to a stack of bills waiting to be paid. Assets are what a company owns or something that’s owed to the company. They include tangible items such as buildings, machinery, and equipment as well as intangibles such as accounts receivable, interest owed, patents, or intellectual property.
